
In an increasingly interdependent global economy, insurance companies face an intricate web of legislative and regulatory requirements to manage their clients’ global insurance programs. Global insurance compliance is a necessity to mitigate risks, avoid legal action, and maintain a strong corporate reputation. To do so, companies need to be continuously vigilant and adaptable. This article outlines why compliance is critical and how global insurance companies can successfully navigate the complex global compliance landscape.
The Challenge
To illustrate how critical global insurer compliance is, we will consider these two trends: foreign direct investment flows to emerging countries and an increasing number of legislation and regulations.
The penalties, as shown in the table below, can be severe for non-compliance, including significant financial fines and potential imprisonment, let alone a resulting potential public relations nightmare. Many of these countries rank in the upper half of the regulatory enforcement ranking, so their laws and regulations should be seriously considered.
Select Emerging Countries’ Inward FDI and Regulatory Environments
|
Country |
FDI Inward Flows, 2023(USD bn) |
Cumulative Growth % 2018-2023 |
Number of Actual or Proposed Insurance Regulatory Changes in 2024 |
Regulatory Enforcement Ranking of 142 Countries |
Penalties for operational non-compliance |
| China (Mainland, Hong Kong) | 163.2 | 18.1 |
38 Mainland 7 Hong Kong |
16 |
Mainland - Fine of USD 143,000 (Mainland and confiscation of assets Hong Kong – Fine of USD 255,428 and 2 years imprisonment (Hong Kong) |
|
India |
28.2 |
-33.2 |
37 |
78 |
Fine of USD 608,495 and confiscation of assets |
|
Brazil |
65.8 |
10.0 |
39 |
68 |
Fine of USD 580,585 |
|
Indonesia |
21.6 |
4.8 |
19 |
47 |
Not specified |
|
Mexico |
36.1 |
5.9 |
5 |
71 |
Criminal offense and fines |
|
South Korea |
15.2 |
24.5 |
17 |
47 |
5 years imprisonment and fines |
|
United Arab Emirates |
30.7 |
295.2 |
13 |
26 |
A fine of USD 272,480 and/or imprisonment. |
|
Vietnam |
18.5 |
19.3 |
11 |
92 |
Administrative and disciplinary penalties or face criminal charges |
What is compliance?
Insurers need to address six key categories of compliance. Each country has its own set of insurance laws and regulations that can vary significantly. Understanding these laws and regulations (and their local nuances and subtleties) is essential to operating compliantly.
Operational compliance. The activities conducted need to adhere to the appropriate licenses and authorisations.
Data security compliance. Adhering to local data privacy and security laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, has become a legal requirement in many countries.
Legally compliant clients and business partners. Clients and business partners (brokers, reinsurers, consultants, captive managers, etc.) need to comply with local laws.
Financial crime compliance. Strong anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing controls are required, such as due diligence, monitoring transactions, and reporting suspicious activities.
Tax compliance. Insurance and tax authorities worldwide have increased their scrutiny of insurance-related transactions, and these developments need to be monitored.
Contract compliance. Any insured’s global insurance program must be designed to accommodate jurisdiction-specific laws and regulations while still being aligned with an organisation’s overall risk finance structure and risk management objectives.
Establishing a robust compliance framework
Below is a visual of the key components of a robust compliance framework.
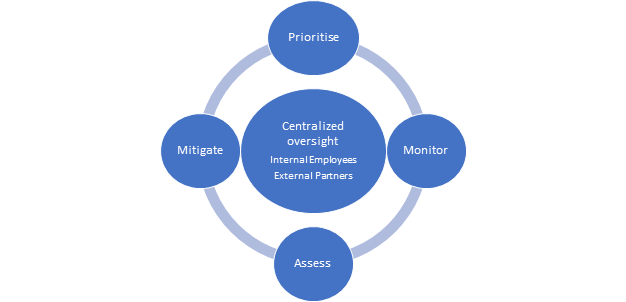
Let’s briefly look at the process and resources needed to ensure compliance. The process starts with a periodic prioritisation of all insureds’ largest exposures across all countries to ensure that the appropriate compliance resources are brought to bear for the remaining steps. Monitoring requires the ongoing review and identification of any changes in the jurisdictional laws and regulations. Then a risk assessment can be undertaken on the current operations if needed to ensure that the appropriate risk mitigation measures, if any, are employed.
To manage this process efficiently, there are three key resources:
Centralised Compliance Team. A centralised team is crucial to create and maintain a compliance culture and coordinate all resources and activities in a cohesive manner. The team needs to develop a compliance culture to support the overall process by assigning accountability, developing policies and procedures, providing training, implementing appropriate information technology and conducting periodic compliance audits.
Internal partners. These resources consist of client service teams, underwriters, global network managers, and those who oversee key insurance processes, such as policy administration, claims and financial matters on both a global and local basis.
External partners. The centralised team needs to identify external resources that could support and provide greater insight, such as understanding the local nuances and language of regulations. These include fronting partners, local regulators, outside local counsel, global and local brokers and outside information providers, such as Axco, that can monitor regulatory developments in over 170 countries and provide some further insight, accordingly.
The Bottom Line
Global insurance compliance is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement. By understanding the regulatory landscape, establishing a robust compliance framework, and fostering a culture of compliance, insurers and their clients can navigate the complexities of international insurance markets and achieve sustainable growth. Embracing digital transformation and leveraging technology solutions will further enhance compliance efforts and ensure long-term success.
Axco is the leading supplier of global insurance market information with over 55 years’ experience in researching and publishing industry intelligence on insurance and employee benefits. Its unique business model and methods of research have enabled the development of an extensive suite of products comprising in-depth reports, focused profiles, Q&A databases, intelligent questioning tools, and email services which are delivered to every corner of the globe.